John Rogers is Developing Tech That Will Dissolve in Water When Obsolete
Laura McQuarrie — July 24, 2013 — Tech
References: sciencemag.org & gizmodo
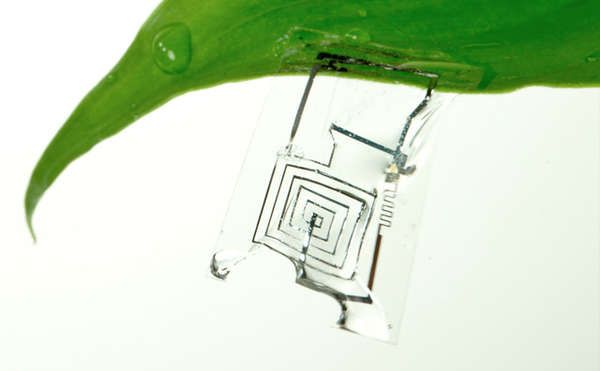
John Rogers is a scientist leading the 'Born to Die' project at the University of Illinois. This project aims to create circuitry that can be dissolved in water.
'Born to Die' addresses the problem of the overabundance of tech available on the market and the waste it leaves behind. As Rogers notes, “you don’t need your cellphone to last for 25 or 50 years.”
The magnesium and silicone circuits are printed on fine layers of silk, which causes them to dissolve slowly when wet. This project aims to make circuitry more organic, and enable it to "wither away like a dead plant." The biggest challenge Rogers' team faces is timing the precise dates of expiry. This is an incredible initiative to reduce the amount of waste that can't be recycled and ends up in landfills.
'Born to Die' addresses the problem of the overabundance of tech available on the market and the waste it leaves behind. As Rogers notes, “you don’t need your cellphone to last for 25 or 50 years.”
The magnesium and silicone circuits are printed on fine layers of silk, which causes them to dissolve slowly when wet. This project aims to make circuitry more organic, and enable it to "wither away like a dead plant." The biggest challenge Rogers' team faces is timing the precise dates of expiry. This is an incredible initiative to reduce the amount of waste that can't be recycled and ends up in landfills.
Trend Themes
1. Water-soluble Circuitry - Developing circuitry that can dissolve in water presents opportunities for minimizing tech waste through environmentally friendly disposal methods.
2. Organic Disintegration - Creating circuitry that withers away like a dead plant opens the door to more sustainable and biodegradable electronic components.
3. Expiry Date Precision - Precision in determining the exact dates of circuitry expiry offers the potential for better planning and management of electronic waste.
Industry Implications
1. Electronics Manufacturing - The electronics manufacturing industry could benefit from integrating water-soluble circuitry into their production processes, reducing waste and environmental impact.
2. Waste Management - The waste management industry has an opportunity to develop specialized processes and facilities for the disposal of water-soluble technology, addressing the growing issue of e-waste.
3. Sustainable Design - The sustainable design industry can explore the use of organic disintegration in the creation of environmentally friendly electronic products with built-in obsolescence.
1.8
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness