Researchers at MIT are Getting Closer to Creating Plant-Based Lighting
Justin Lam — February 1, 2018 — Tech
References: news.mit.edu & dezeen
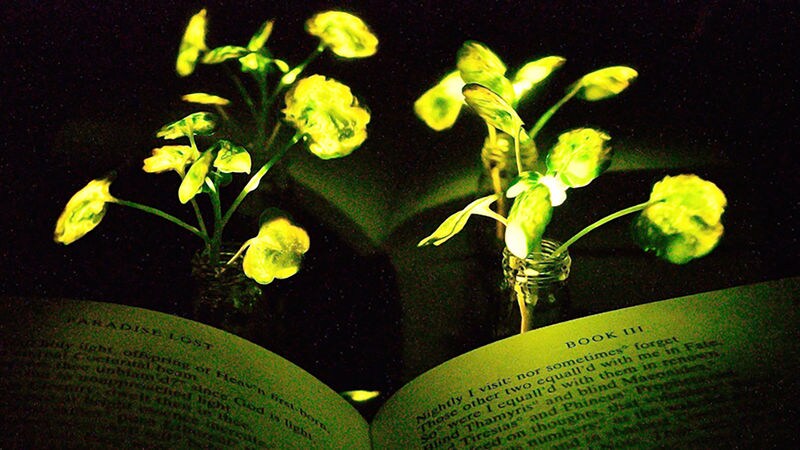
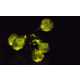
Luminescent plants may soon be available as specialists at MIT have taken the first steps in turning plants into functional lights. Fitting into the field of nanobionics, these new experiments embed plants with a firefly enzyme causing the leaves to glow. Current research has caused plants to glow for nearly four hours, and continued work in this field may eventually lead to low-intesity indoor lighting.
To create the luminescent plants, researchers impregnate plants with a solution comprised of luciferase -- the enzyme that grants fireflies luminescence -- and nanoparticles. The result of this combination leads to a dim light projected off the leaves of the plant. Current testing has been focused on leafy greens and was been be used on argula, kale, spinach and watercress.
The plan for this research is to eventually have plants act as efficient and viable sources of light. For ecological reasons this makes sense as plants can self repair, produce their own energy and do not require man made power. Further research intends to discover a way to inhibit the luciferase nanoparticles so users can turn off the light. These further explorations will hopefully lead to widespread use of luminescent plants as a replacement for man made lighting.
To create the luminescent plants, researchers impregnate plants with a solution comprised of luciferase -- the enzyme that grants fireflies luminescence -- and nanoparticles. The result of this combination leads to a dim light projected off the leaves of the plant. Current testing has been focused on leafy greens and was been be used on argula, kale, spinach and watercress.
The plan for this research is to eventually have plants act as efficient and viable sources of light. For ecological reasons this makes sense as plants can self repair, produce their own energy and do not require man made power. Further research intends to discover a way to inhibit the luciferase nanoparticles so users can turn off the light. These further explorations will hopefully lead to widespread use of luminescent plants as a replacement for man made lighting.
Trend Themes
1. Nanobionics - Exploring the field of nanobionics could lead to disruptive innovation opportunities in creating luminescent plants and other applications.
2. Bio-inspired Lighting - Developing bio-inspired lighting using plant-based technology could revolutionize the indoor lighting industry and provide sustainable alternatives.
3. Self-sustaining Plants - Research on self-sustaining plants as sources of light presents opportunities for disruptive innovations in energy-efficient and environmentally friendly lighting solutions.
Industry Implications
1. Lighting Industry - The lighting industry can explore the potential of luminescent plants as a disruptive innovation for low-intensity indoor lighting.
2. Agriculture Industry - The agriculture industry can leverage the research on impregnating plants with enzymes and nanoparticles to develop new applications for plant-based technologies.
3. Sustainability Industry - The sustainability industry can benefit from the development of self-sustaining plants as a renewable and eco-friendly source of lighting.
4.4
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness