Temple University Developed a Method for Making 3D-Printed Bandages
Laura McQuarrie — April 13, 2018 — Tech
References: temple-news & 3ders.org
Thanks to constantly evolving developments in the world of additive manufacturing, one-size-fits-all bandages have the potential to be phased out and replaced by highly personalized 3D-printed bandages.
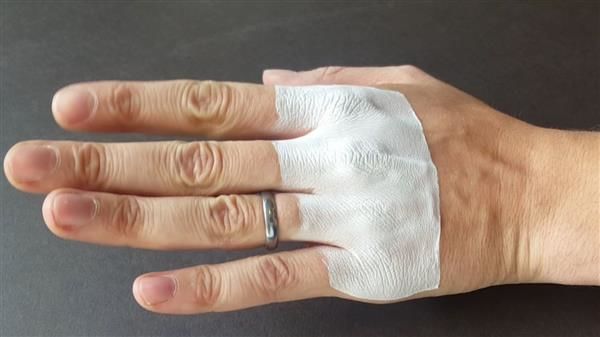
Researchers from the bio-engineering department at Philadelphia's Temple University have developed a new method of making 3D-printed bandages with a custom 3D printer. Unlike the protective strips of materials that are sold in pharmacies, which can be awkward to apply to some injuries, the flexible, lightweight 3D-printed bandages can be printed directly onto a patient's skin for a perfectly natural fit. As such, these solutions are not only comfortable but speed up the healing process.
As part of its work, the research team has also developed a handheld version of the custom-built 3D printer that has the potential to be available for commercial applications in the future.
Researchers from the bio-engineering department at Philadelphia's Temple University have developed a new method of making 3D-printed bandages with a custom 3D printer. Unlike the protective strips of materials that are sold in pharmacies, which can be awkward to apply to some injuries, the flexible, lightweight 3D-printed bandages can be printed directly onto a patient's skin for a perfectly natural fit. As such, these solutions are not only comfortable but speed up the healing process.
As part of its work, the research team has also developed a handheld version of the custom-built 3D printer that has the potential to be available for commercial applications in the future.
Trend Themes
1. Personalized Bandages - The development of 3D-printed bandages allows for highly personalized solutions, fitting perfectly to a patient's injury for improved comfort and faster healing.
2. Additive Manufacturing - The advancements in additive manufacturing enable the production of custom bandages with flexible and lightweight materials, leading to innovative medical applications.
3. On-skin Printing - The ability to 3D print bandages directly onto a patient's skin offers convenient and effective wound care, bypassing the need for traditional bandage application methods.
Industry Implications
1. Healthcare - The healthcare industry can leverage 3D printing technology to create personalized bandages that optimize patient care and healing outcomes.
2. Additive Manufacturing - The additive manufacturing industry can explore opportunities in the production of custom medical devices, such as 3D-printed bandages, for the healthcare sector.
3. Medical Technology - Medical technology companies can develop handheld 3D printing devices for commercial applications, offering convenience and accessibility in the healthcare field.
3.1
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness