NASA Tests Redwire's New Printer That Uses Moon Dust to Make Material
Niko Pajkovic — August 17, 2021 — Tech
References: nasa & digitaltrends
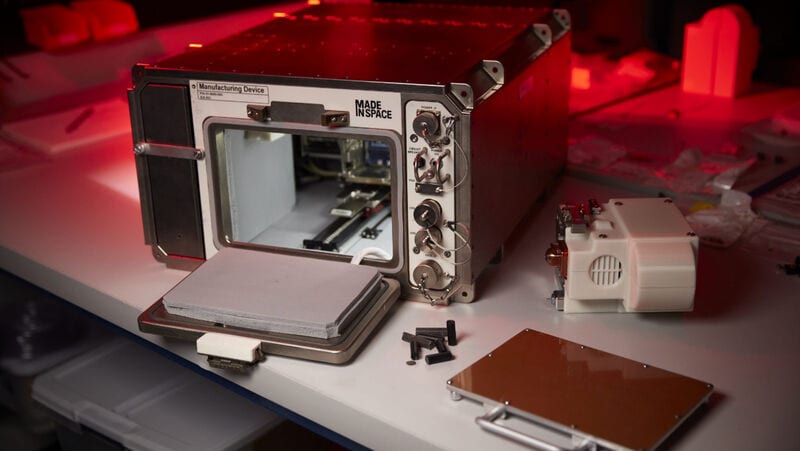
NASA has announced that it is currently testing a specialty 3D printer made by Redwire, an American aerospace manufacturer based in Jacksonville, Florida. Designed specifically for space travel, the printer is capable of using moon dust -- technically known as regolith -- as its raw material for producing solid objects.
The idea behind this one-of-a-kind printer was to save NASA from having to ship out heavy 3D printing equipment into space. Instead, the machine would be operational with the already exiting materials found on the moon. The printer has been trained on a moon dust simulant, an earth-made material that is meant to mimic regolith.
While the printer is only capable of producing small fixtures and fittings, Redwire hopes that the technology -- once further developed -- will be capable of generating complex parts such as landing pads, roads, and other foundations.
Image Credit: Redwire
The idea behind this one-of-a-kind printer was to save NASA from having to ship out heavy 3D printing equipment into space. Instead, the machine would be operational with the already exiting materials found on the moon. The printer has been trained on a moon dust simulant, an earth-made material that is meant to mimic regolith.
While the printer is only capable of producing small fixtures and fittings, Redwire hopes that the technology -- once further developed -- will be capable of generating complex parts such as landing pads, roads, and other foundations.
Image Credit: Redwire
Trend Themes
1. Made-for-space 3D Printing Technologies - Space exploration and colonization will require affordable, lightweight, and convenient manufacturing techniques and materials that are readily available off-planet.
2. Moon-based Manufacturing Processes - Manufacturing processes and equipment that use raw materials found on the Moon and other celestial bodies will reduce the cost and risks of space exploration and exploitation.
3. Miniaturized 3D Printing - The development of small, yet powerful 3D printers has widespread applications, from on-demand production of spare parts in remote locations to the creation of customized products on-site in various industries.
Industry Implications
1. Space Exploration and Colonization - 3D printing and manufacturing technologies that can operate in space and use in-situ resources such as moon dust are essential for establishing permanent settlements and infrastructure on the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
2. Aerospace and Defense - Advanced 3D printing and additive manufacturing technologies can enhance the efficiency, reliability, and safety of space vehicles, satellites, and other aerospace systems, as well as reduce their weight and manufacturing costs.
3. Construction and Infrastructure - The use of 3D printing for construction and infrastructure projects has the potential to revolutionize the building industry, from reducing waste and labor to enabling new forms of design and customization.
2.6
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness