Corroding Biobattery Delivery
Michael Plishka — December 4, 2008 — Lifestyle
References: newscientist
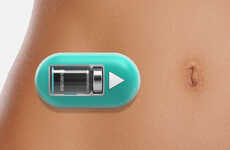
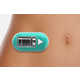
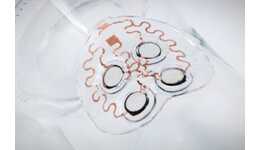
While most implanted drug delivery devices corrode when implanted in the body, a new type of “biobattery” takes advantage of the corrosion and uses the corrosion process as a time-release system.
When the magnesium polymer is exposed to bodily fluids, a very predictable and stable electric current is generated. This current reverses the electrostatic charges that bind the drug to the polymer aspect of the battery. With the charges reversed, the drugs are released into the body to do their thing.
This battery actually can be used with those implants in the body that already corrode, such as Titanium hips or knees.
When the magnesium polymer is exposed to bodily fluids, a very predictable and stable electric current is generated. This current reverses the electrostatic charges that bind the drug to the polymer aspect of the battery. With the charges reversed, the drugs are released into the body to do their thing.
This battery actually can be used with those implants in the body that already corrode, such as Titanium hips or knees.
Trend Themes
1. Biobattery Drug Delivery - Corrosion process utilized in biobattery drug delivery presents opportunity for more predictable and stable drug release system.
2. Smart Implantable Devices - Development of biobattery drug delivery system reflects trend towards smarter implantable devices.
3. Electrochemical Drug Release - Use of electrochemical current to release drugs from implanted devices opens up possibilities for more precise drug dosing and personalized treatment plans.
Industry Implications
1. Medical Devices - Biobattery drug delivery system presents disruptive innovation opportunity for medical device manufacturers to develop smarter and more effective implantable devices.
2. Pharmaceuticals - Electrochemical drug release presents new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to develop drugs tailored for use with implantable devices.
3. Materials Science - Development of biodegradable and corrosion-resistant materials for implants presents an opportunity for materials scientists to support the growing field of smart and sustainable medical devices.
1.1
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness