Skype Call Captioning Aids Those who are Hard of Hearing or Deaf
Michael Hemsworth — December 5, 2018 — Tech
References: blogs.skype & slashgear
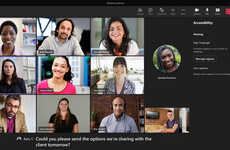
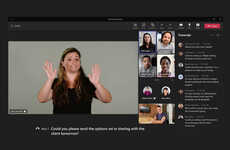
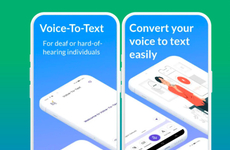
The Skype call captioning functionality has been announced by Microsoft for users who are deaf or hard of hearing to help them maintain optimal connectivity when chatting with colleagues or friends in real-time.
The new feature was announced by the company on UN International Day of Persons with Disabilities (December 3) and works by automatically converting a persons speech into subtitles and captions. The scrolling functionality will always keep the most recently spoken words on the top with previous captions floating nearby to keep users informed during the entire call.
The Skype call captioning functionality will work on Skype version 8 and will be available for use across 20 different dialects and languages to make it internationally compatible.
The new feature was announced by the company on UN International Day of Persons with Disabilities (December 3) and works by automatically converting a persons speech into subtitles and captions. The scrolling functionality will always keep the most recently spoken words on the top with previous captions floating nearby to keep users informed during the entire call.
The Skype call captioning functionality will work on Skype version 8 and will be available for use across 20 different dialects and languages to make it internationally compatible.
Trend Themes
1. Real-time Subtitles for Video Chatting - Opportunity for companies to integrate real-time speech-to-text technology into their video conferencing softwares.
2. Accessibility in Communication - Potential for businesses to address the needs of people with hearing disabilities.
3. Artificial Intelligence for Real-time Captioning - Prospect for AI-powered captioning softwares to become more accurate and widely used for video conferencing applications.
Industry Implications
1. Telecommunications - Industry players can leverage the subtitle feature in video conferencing services to expand accessibility options and enhance user experience.
2. Healthcare - Medical institutions can use real-time captioning technology in telemedicine consultations for patients with hearing disabilities.
3. Education - Schools and universities can use real-time captioning technology to improve accessibility in virtual classrooms for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
2
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness