Biofuels are Accessed Through Dissolving Cyanobacteria
Katherinev123 — December 11, 2009 — Eco
References: eurekalert.org & green.myninjaplease
The idea of self-destructing bacteria sounds good. I mean, who wants bacteria to keep growing—anywhere? But in the case of biofuel-producing bacteria, it's an especially fantastic concept, which is why Cyanobacteria was created.
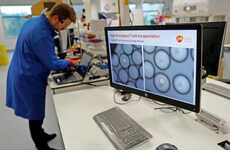
Cyanobacteria was developed by researchers at Arizona State University. It's a self-destructing bacteria that dissolves from the inside out, which makes it substantially easier to access the high-energy fats and biofuel byproducts within it. The development of Cyanobacteria stands to be seriously beneficial for fuel production since it has a higher yield potential than most biofuels being tested today.
Click through the gallery to see what Cyanobacteria looks like (shudder).
Cyanobacteria was developed by researchers at Arizona State University. It's a self-destructing bacteria that dissolves from the inside out, which makes it substantially easier to access the high-energy fats and biofuel byproducts within it. The development of Cyanobacteria stands to be seriously beneficial for fuel production since it has a higher yield potential than most biofuels being tested today.
Click through the gallery to see what Cyanobacteria looks like (shudder).
Trend Themes
1. Self-destructing Bacteria - Opportunity for developing self-destructing bacteria for various applications in industries.
2. Biofuel Production - Opportunity for innovating new methods and technologies to increase biofuel production efficiency.
3. High-yield Biofuels - Potential for developing biofuels with higher yield potential compared to existing alternatives.
Industry Implications
1. Biotechnology - Disruptive innovation opportunities in the development and application of self-destructing bacteria.
2. Energy - Opportunity for disruptive innovation in biofuel production using self-destructing bacteria.
3. Environmental - Potential for developing sustainable and high-yield biofuels to reduce environmental impact.
2.5
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness