UpNano and BIO INX Debut a New Bio-Ink for Organ-on-Chip Bioprinting
UpNano and BIO INX have teamed up to create a new bio-ink for organ-on-chip bioprinting. Developed as a result of the collaboration, the bio-ink introduces unique capabilities for two-photon polymerization (2PP) 3D printing. One of the key strengths of the Hydrotech INX U200 lies in its compatibility with biological materials and its biocompatible nature. This critical attribute ensures the safe integration of the bio-ink with living cells and tissues, mitigating any potential adverse reactions.
Moreover, this advanced bio-ink facilitates the precise and detailed printing of structures at both micro and medium scales, unlocking the ability to create complex and intricate biological architectures.
As this innovative product continues to be explored and adopted, it has the potential to revolutionize the field of tissue engineering and contribute to advancements in regenerative medicine.
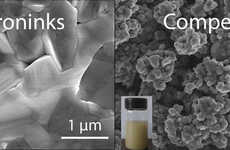
Image Credit: UpNano, BIO INX
Moreover, this advanced bio-ink facilitates the precise and detailed printing of structures at both micro and medium scales, unlocking the ability to create complex and intricate biological architectures.
As this innovative product continues to be explored and adopted, it has the potential to revolutionize the field of tissue engineering and contribute to advancements in regenerative medicine.
Image Credit: UpNano, BIO INX
Trend Themes
1. Bioprinting Advancements - The development of biocompatible bio-ink for organ-on-chip bioprinting opens up new possibilities for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
2. Two-photon Polymerization (2PP) Printing - The use of two-photon polymerization printing technology allows for precise and detailed printing of complex biological architectures.
3. Safe Integration of Bio-inks - The compatibility of the Hydrotech INX U200 bio-ink with biological materials ensures safe integration with living cells and tissues, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Industry Implications
1. Biomedical Engineering - The development of biocompatible bio-inks presents disruptive innovation opportunities in the field of biomedical engineering, particularly in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
2. 3D Printing - The advancement of two-photon polymerization printing technology has the potential to disrupt the 3D printing industry, specifically in the printing of intricate biological structures.
3. Pharmaceuticals - The safe integration of bio-inks opens up new avenues for pharmaceutical research and development, allowing for more accurate testing of pharmaceutical products on human tissue models.
2.6
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness