MIT & MicroChips Testing MEMS For Meds
References: technologyreview
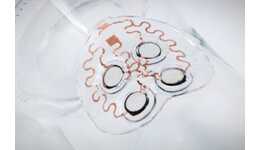
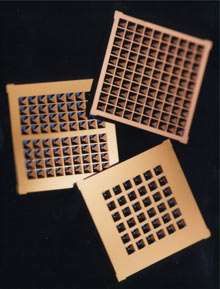
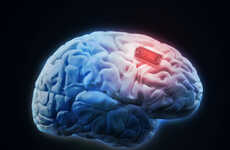
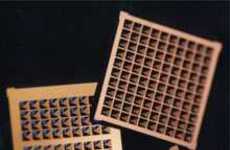
The day when taking your meds is as simple as inserting a chip under your skin is getting closer. MIT, along with MicroChips, is testing a medical implant using microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) to deliver even dosage of medications.
Animal testing is set to begin in January to see if they can heal osteoporosis-derived bone damage, and in a year and a half, MIT wants to start testing implants on diabetic humans to regulate blood sugar.
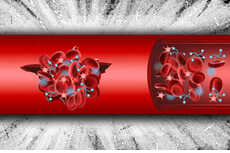
"The first product, a device for delivering an anti-osteoporosis drug automatically, could allow patients to replace 500 daily injections with a single outpatient implant procedure," according to Technology Review. "The glucose sensor, by continuously monitoring glucose levels, could reveal spikes in blood-sugar levels that go undetected using conventional sensors. Such spikes, if not treated, can contribute to organ damage, including blindness."
Those are only two potential applications, MIT anticipates the use of MEMs to deliver multiple drugs at once, detect early signs of heart attacks and strokes.
Animal testing is set to begin in January to see if they can heal osteoporosis-derived bone damage, and in a year and a half, MIT wants to start testing implants on diabetic humans to regulate blood sugar.
"The first product, a device for delivering an anti-osteoporosis drug automatically, could allow patients to replace 500 daily injections with a single outpatient implant procedure," according to Technology Review. "The glucose sensor, by continuously monitoring glucose levels, could reveal spikes in blood-sugar levels that go undetected using conventional sensors. Such spikes, if not treated, can contribute to organ damage, including blindness."
Those are only two potential applications, MIT anticipates the use of MEMs to deliver multiple drugs at once, detect early signs of heart attacks and strokes.
Trend Themes
1. Drug-delivering Implants - MEMS technology can revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry by enabling medical implants to deliver dosages of various drugs and monitor vital signs continuously.
2. Non-invasive Drug Delivery - MEMS can allow for the development of non-invasive drug delivery systems, reducing the need for daily injections, providing better patient compliance and experience.
3. Continuous Vital Signs Monitoring - The use of MEMS technology in medical implants can revolutionize healthcare by allowing for the continuous monitoring of vital signs, detecting early signs of potentially lethal diseases and alerting the patient or healthcare provider.
Industry Implications
1. Pharmaceutical - The pharmaceutical industry will benefit from the development of MEMS-based drug delivery systems that can replace traditional methods, improve accuracy, compliance, and reduce healthcare costs.
2. Medical Devices - Medical device manufacturers can leverage MEMS technology to develop innovative and disruptive implantable devices enabling drug delivery and vital signs monitoring in a non-invasive way.
3. Healthcare - The healthcare industry can benefit from the development of MEMS-based devices that enable continuous vital sign monitoring, facilitate disease diagnosis, and the delivery of personalized treatments.
1.9
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness